Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement (SAVR) is a type of heart surgery in which the diseased valve is replaced by opening the patient's chest. SAVR is often the best choice for patients with severe valve disease.
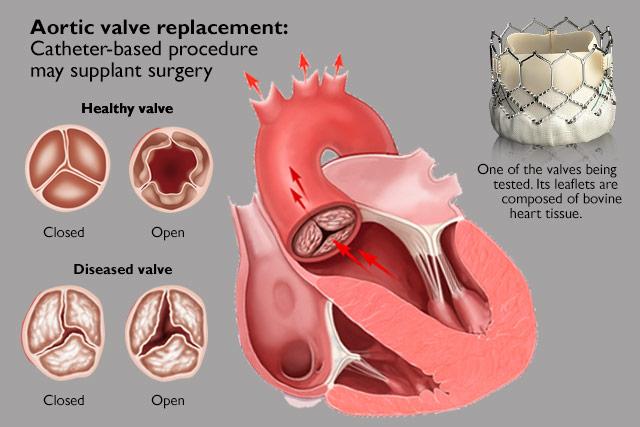
However, the surgery causes significant trauma and may lead to serious postoperative complications, which means patients need to undergo strict postoperative management. So, what are the common postoperative management measures?
What is the in-hospital management after surgical aortic valve replacement?
After undergoing open-chest surgery, patients typically spend 1 day or even longer in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). After leaving the ICU, they will be transferred to a regular ward for several days.

During hospitalization, medical staff will continue to take some supervisory care measures, including:
Checking for wound infection;
Regular monitoring of the patient's blood pressure, respiration, and heart rate;
Relieving postoperative pain through medication, massage, or changing positions;
Encouraging regular ambulation, such as walking, and gradually increasing exercise;
Encouraging patients to do breathing exercises to restore their cardiopulmonary function.
In general, patients can be discharged and return home within 4-7 days.
Once complications such as thromboembolism, cardiac block, bleeding, and perivalvular regurgitation occur, it is necessary for patients to continue treatment under the guidance of a physician, even considering undergoing surgical treatment again when the artificial valve does not match the heart.
After discharge, what should patients do?
1.Common postoperative precautions
Immediately after discharge, Patients may experience pain, swelling, and redness in incision, possibly accompanied by a poor appetite, easy fatigue, and insomnia. There is no need for patients to overreact to those common postoperative symptoms, just follow the physicians' instructions for recuperation, and seek their help if these symptoms severely affect daily life.
If the patient's body recovers smoothly, the sternum injured due to the surgical operation will heal in 6-8 weeks, but complete recovery may take 3 months or even longer. Do not lift anything heavier than 4kg for several weeks after the operation, and do not carry heavy objects for 4-6 months after the operation to avoid damaging the sternum.
After 8 weeks, the patient can return to work or drive with good physical condition assessed by the physician. However, if the patient's work is strenuous, at least 3 months of recovery and permission from the physician are required before returning to work.
Since infection is common after valve replacement surgery, maintaining oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings are essential for preventing endocarditis. Patients should consult their physicians about what toothbrush to choose and how to brush their teeth to reduce the risk of infection. If the patient needs to undergo dental procedures or other surgical operations, they must inform their primary care physician and cardiologist.
2.Improvement in lifestyle habits
During the recovery period, physicians will recommend that patients improve some lifestyle measures to help with postoperative recovery, which may include physical exercise, healthy diet, disease education, emotional and stress management, and smoking and alcohol cessation.
Generally, walking and tai chi are low-risk exercises during the postoperative recovery period. As physical function further recovers, jogging and cycling may also be recommended as part of the cardiac rehabilitation program.
A healthy diet requires limiting high-fat, high-sugar, and high-salt foods, and consuming foods rich in protein and vitamins will help with the patient's physical recovery.
3. Regular follow-up
The first outpatient follow-up should be scheduled 6 weeks to 3 months after surgery. Patients who need to start working or driving as soon as possible should visit the hospital for a check-up, including the medical history after discharge, physical examination, appropriate blood tests, and transthoracic echocardiography, with an electrocardiogram if necessary at least 6 weeks after the operation. After the initial examination, follow-up examinations should be done at 6, 9, and 12 months postoperatively, and then annually thereafter, according to the physician's instructions.
4. Medication management
Most patients need to take anticoagulant drugs long-term after surgery to reduce the formation of blood clots. Common drugs include warfarin and aspirin. Low-dose aspirin is suitable for all patients undergoing prosthetic valve replacement surgery to prevent clot formation, while warfarin is often used in patients with mechanical valves or those prone to clot formation.
Follow the prescribed medication regimen strictly, and do not change the daily dosage, method of administration, or other concomitant medications without authorization. Contact the physician for advice if forgetting or missing a dose. Patients using warfarin also need regular blood tests because the drug's effectiveness can change over time. In some cases, such as when taking antibiotics or changing diet, additional blood tests may be necessary. If the dose is incorrect, the medication may not work or may cause serious bleeding.
5. Prompt medical attention
Seek medical attention promptly if new symptoms or signs appear that may be related to postoperative complications, such as fever, chills, any infections (such as dental and skin infections), changes in mechanical valve sounds, shortness of breath, decreased exercise capacity, stroke symptoms, palpitations, or chest pain.
©Copyright 1998-2023, MicroPort CardioFlow Medtech Corporation. All rights reserved. | 网站备案/许可证号:沪ICP备2023023560号  沪公网安备 31011502014876号
沪公网安备 31011502014876号
互联网药品信息服务资格证书编号:(沪)-非经营性 - 2024 - 0135
“MicroPort CardioFlow”及“  are registered trademarks of MicroPort CardioFlow Medtech Corporation.
are registered trademarks of MicroPort CardioFlow Medtech Corporation.