Atrial fibrillation, one of the most common arrhythmias in clinical practice, refers to the loss of regular, organized electrical activity in the atria, replaced by rapid, irregular fibrillation waves. It is typically characterized by an irregular and fast heart rate, caused by the atria losing their normal rhythm. Organic heart disease, autoimmune diseases, trauma, smoking, alcohol abuse, and family history are all factors that can lead to AF. Thromboembolism is the most significant complication of AF, with the highest incidence and greatest harm being stroke.
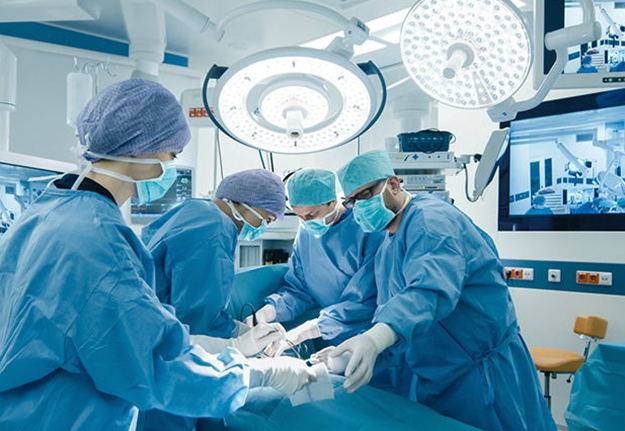
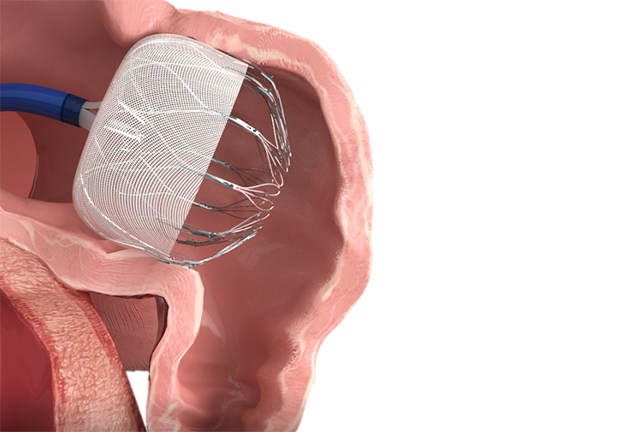
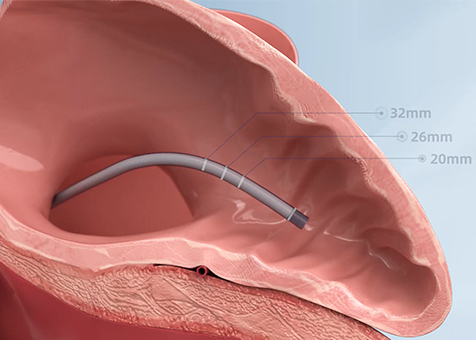
Studies have shown that 90% of thrombi in non-valvular AF patients originate from the left atrial appendage (LAA). A large data study on LAA thrombus before pulmonary vein isolation in 2019 once again confirmed that 100% of thrombus formation in AF patients originates from the LAA.
1.AF causes blood to stagnate in the LAA, gradually forming a thrombus
2.The unique anatomy of the LAA and its uneven internal musculature create eddies in the blood, promoting thrombus formation
3.Thrombi dislodge from the LAA and enter the arterial system
4.Thrombi become lodged in the cerebral vasculature, restricting blood flow and causing stroke












 沪公网安备 31011502014876号
沪公网安备 31011502014876号 are registered trademarks of MicroPort CardioFlow Medtech Corporation.
are registered trademarks of MicroPort CardioFlow Medtech Corporation.